体内巨噬细胞清除剂 Clodronate Liposomes(From Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam)
产品说明书
FAQ
COA
已发表文献
Clodronate Liposomes是由荷兰阿姆斯特丹Vrije University 的Nico van Rooijen教授开发,利用巨噬细胞的内吞机制,将膜不通透性的氯膦酸(clodronate)带入细胞内。在巨噬细胞溶酶体磷酸酶的作用下,释放溶解在脂质体水相中的氯膦酸,并累积在细胞内。当其达到一定浓度时可以诱导巨噬细胞进入凋亡过程,从而达到清除巨噬细胞的功能。
Clodronate Liposomes适用于多种注射方式,如静脉注射、腹腔注射、皮下注射、鼻内注射和睾丸等。注射量与小鼠的体重、注射周期、注射方式以及实验目的有关。
产品性质
|
溶液(Solution) |
10 mM Na2HPO4,10 mM NaH2PO4,140 mM NaCl |
|
浓度(Concentration) |
5 mg/mL |
|
脂类成分(Lipid composition) |
磷脂酰胆碱和胆固醇 |
|
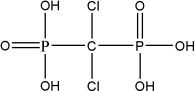
结构式(Structure) |
|
运输和保存方法
产品4 ℃保存。冰袋运输。不能冻存!保质期6个月。
注意事项
1)为了您的安全和健康,请穿实验服并戴一次性手套操作。
2)使用前一定要充分混匀并恢复到室温。
3)本产品仅用于科研用途,禁止用于人身上。
产品使用
【具体注射量请参考相关文献,并根据自身实验条件(如实验目的,注射方式,注射周期)进行摸索和优化。
腹腔注射
1.注射前,将Clodronate Liposomes和无菌PBS(注射用)从冰箱中取出。自然回温到室温(18 ℃)。
【注】:Clodronate Liposomes悬液禁止冻存,也不能超过30 ℃。
2.上下颠倒8-10次混匀。将26 Gauge针头连接到1ml的注射器上,吸取200 μl的Clodronate Liposomes。
3.用左手抓取小鼠耳后足够多的皮肤和尾巴,固定头部和四肢。
4.将小鼠微微倾斜,让头部朝向地面,使得原本集中在腹部右下方的器官向头部方向移动,远离注射位点。
5.注射前将注射器颠倒6次,将Clodronate Liposomes混匀。
【注】:长时间的放置,会使脂质体在注射器中发生沉淀,导致注射时浓度不均一。
6.针头成30度角插入腹部右下方。分别注射200 μL Clodronate Liposomes(实验组)和PBS(对照组)。
参考文献
[1] Song C, Li H, Li Y, et al. NETs promote ALI/ARDS inflammation by regulating alveolar macrophage polarization[J]. Experimental Cell Research, 2019, 382(2): 111486.
[2] Jiang P, Gao W, Ma T, et al. CD137 promotes bone metastasis of breast cancer by enhancing the migration and osteoclast differentiation of monocytes/macrophages[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(10): 2950.
[3] Yang L, Dong C, Tian L, et al. Gadolinium Chloride Restores the Function of the Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication between Hepatocytes in a Liver Injury[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(15): 3748.
[4] Wu H, Xu X, Li J, et al. TIM4 blockade of KCs combined with exogenous TGFβ injection helps to reverse acute rejection and prolong the survival rate of mice receiving liver allografts[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2018, 42(1): 346-358.
[5] Tian L, Li W, Yang L, et al. Cannabinoid receptor 1 participates in liver inflammation by promoting M1 macrophage polarization via RhoA/NF-κB p65 and ERK1/2 pathways, respectively, in mouse liver fibrogenesis[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2017, 8: 1214.
[6] Li W, Chang N, Tian L, et al. miR-27b-3p, miR-181a-1-3p, and miR-326-5p are involved in the inhibition of macrophage activation in chronic liver injury[J]. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2017, 95(10): 1091-1105.
相关产品
|
产品名称 |
产品编号 |
规格 |
|
Control Liposomes (PBS) 体内巨噬细胞清除剂空白脂质体对照 |
40338ES05 |
5 mL |
|
40338ES10 |
10 mL |
HB220530
Clodronate Liposomes是由荷兰阿姆斯特丹Vrije University 的Nico van Rooijen教授开发,利用巨噬细胞的内吞机制,将膜不通透性的氯膦酸(clodronate)带入细胞内。在巨噬细胞溶酶体磷酸酶的作用下,释放溶解在脂质体水相中的氯膦酸,并累积在细胞内。当其达到一定浓度时可以诱导巨噬细胞进入凋亡过程,从而达到清除巨噬细胞的功能。
Clodronate Liposomes适用于多种注射方式,如静脉注射、腹腔注射、皮下注射、鼻内注射和睾丸等。注射量与小鼠的体重、注射周期、注射方式以及实验目的有关。
产品性质
|
溶液(Solution) |
10 mM Na2HPO4,10 mM NaH2PO4,140 mM NaCl |
|
浓度(Concentration) |
5 mg/mL |
|
脂类成分(Lipid composition) |
磷脂酰胆碱和胆固醇 |
|
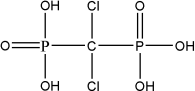
结构式(Structure) |
|
运输和保存方法
产品4 ℃保存。冰袋运输。不能冻存!保质期6个月。
注意事项
1)为了您的安全和健康,请穿实验服并戴一次性手套操作。
2)使用前一定要充分混匀并恢复到室温。
3)本产品仅用于科研用途,禁止用于人身上。
产品使用
【具体注射量请参考相关文献,并根据自身实验条件(如实验目的,注射方式,注射周期)进行摸索和优化。
腹腔注射
1.注射前,将Clodronate Liposomes和无菌PBS(注射用)从冰箱中取出。自然回温到室温(18 ℃)。
【注】:Clodronate Liposomes悬液禁止冻存,也不能超过30 ℃。
2.上下颠倒8-10次混匀。将26 Gauge针头连接到1ml的注射器上,吸取200 μl的Clodronate Liposomes。
3.用左手抓取小鼠耳后足够多的皮肤和尾巴,固定头部和四肢。
4.将小鼠微微倾斜,让头部朝向地面,使得原本集中在腹部右下方的器官向头部方向移动,远离注射位点。
5.注射前将注射器颠倒6次,将Clodronate Liposomes混匀。
【注】:长时间的放置,会使脂质体在注射器中发生沉淀,导致注射时浓度不均一。
6.针头成30度角插入腹部右下方。分别注射200 μL Clodronate Liposomes(实验组)和PBS(对照组)。
参考文献
[1] Song C, Li H, Li Y, et al. NETs promote ALI/ARDS inflammation by regulating alveolar macrophage polarization[J]. Experimental Cell Research, 2019, 382(2): 111486.
[2] Jiang P, Gao W, Ma T, et al. CD137 promotes bone metastasis of breast cancer by enhancing the migration and osteoclast differentiation of monocytes/macrophages[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(10): 2950.
[3] Yang L, Dong C, Tian L, et al. Gadolinium Chloride Restores the Function of the Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication between Hepatocytes in a Liver Injury[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(15): 3748.
[4] Wu H, Xu X, Li J, et al. TIM4 blockade of KCs combined with exogenous TGFβ injection helps to reverse acute rejection and prolong the survival rate of mice receiving liver allografts[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2018, 42(1): 346-358.
[5] Tian L, Li W, Yang L, et al. Cannabinoid receptor 1 participates in liver inflammation by promoting M1 macrophage polarization via RhoA/NF-κB p65 and ERK1/2 pathways, respectively, in mouse liver fibrogenesis[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2017, 8: 1214.
[6] Li W, Chang N, Tian L, et al. miR-27b-3p, miR-181a-1-3p, and miR-326-5p are involved in the inhibition of macrophage activation in chronic liver injury[J]. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2017, 95(10): 1091-1105.
相关产品
|
产品名称 |
产品编号 |
规格 |
|
Control Liposomes (PBS) 体内巨噬细胞清除剂空白脂质体对照 |
40338ES05 |
5 mL |
|
40338ES10 |
10 mL |
HB220530
Q:做肝脏巨噬细胞清除需要灌流,还有流式有没有什么建议?
A:没有灌注,流式毫无意义,因为巨噬细胞没有分到,怎么看差异。流式建议检测F4/80和CD11b。推荐尾静脉注射,24h后取肝脏,做免疫组化。免疫组化不用灌流。
Q:体内巨噬细胞清除剂空白脂质体对照这个是单室脂质体还是多室脂质体?
A: 多室的。
Q:巨噬细胞清除剂的浓度是多少?
A: 5mg/mL。
Q: Clodronate Liposomes(From Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam) 体内巨噬细胞清除剂这个产品的脂质体粒径是多大?
A: 150nm~3um.
Q:收到 Clodronate liposomes 后该如何保存 操作?
A:收到氯磷酸脂质体后,如果不能马上使用,需放置在 4℃冰箱。禁止冻存!使用时作为原液使用, 不能进行稀释。脂质体很容易发生沉淀,建议使用之前轻轻混匀,另外 4℃的氯磷酸脂质体不能马上使用,需要恢复到室温才能进行注射。
Q:Clodronate liposomes 能否用于体外巨噬细胞清除?
A:产品可以用于体外巨噬细胞的清除,但是这种方法比较适合体内实验。主要是由于在体外培养过程中,从死亡细胞释放的氯磷酸或者是从脂质体中“渗漏”出来氯磷酸,会一直存在于培养基中,但是在体内,氯磷酸的半衰期很短,很快就会被肾脏清除。虽然游离的氯磷酸不会进入细胞也不会进入脂质体,但是一旦他们在培养基中积累就会慢慢地进入细胞中。
Q:在静脉注射 Clodronate liposomes 后动物很快就死亡了,是什么原因?
A:一方面有可能是动物注射了不均一的脂质体悬液。建议在使用之前轻轻摇晃混匀。脂质体在体外 一段时间后会发生沉降。如果在很长一段时间内需要一次注射多只动物,那么脂质体便会在注射器中 发生沉淀,形成不均一悬液,这样一来,第一只注射的计量与最后一只注射的计量就会发生明显的变 化。另外一方面有可能是脂质体刚从冰箱取出后,没有恢复到室温。
Q:对于清除不同器官或是组织内的巨噬细胞应该注射什么位置,注射剂量多少,注射时间和周期如何确定?
A:这个要涉及到具体的实验方案设计,建议客户自行设计实验方案,我们可以提供给他一些参考文
献或是自行寻找符合自己实验目的的文献进行参考。
Q:动物在注射 Clodronate liposomes 后几天就死亡了?
A:这个可能是操作过程中受到细菌的污染,体内清除巨噬细胞后会增加例如病毒粒子 细菌或者酵母
感染的几率。
Q:静脉注射 Clodronate liposomes 后大鼠脾脏/肝脏中的 ED1+细胞并没有完全消失?
A:大鼠中成熟的巨噬细胞呈现 ED1 和 ED2 双阳性,但是有一些没有吞噬功能的或者吞噬作用小的前体细胞也是 ED1+,但是呈现 ED2-。因此,所有 ED2+的细胞都可以被完全清除,但是 ED1+的细胞却只能被部分清除,清除的比率取决于前体/成熟巨噬细胞的比例。
Q:Clodronate liposomes 没有达到期望的效果?
A:氯磷酸脂质体都是大批量的生产,每批次都会对氯磷酸的浓度以及一些可能的污染物进行检测,确保无误后才会销售给客户。另外,脂质体容易收到极端温度的影响。正确的运输和储存方式:4~8℃,悬液既不能被冻存,也不能被加热超过 30℃。自收到货物起,需要在 3 个月内使用完,不然有可能会影响使用的效果。
Q:在静脉注射时,能不能增加注射的体积?
A:静脉注射时需要依据动物的体重,不能超过 0.1ml/10mg,但是进行腹腔注射可以适当的增加注射
的体积。皮下注射需要根据注射位点的容量进行决定。
Q: 巨噬细胞清除剂,运输的过程中产品冻上了,是不是不能用了?
A:是的,不能用了,只能报废。
Q: 巨噬细胞清除剂是阴离子么,我看是脂质体包裹的,应该是负电吧
A: 是的,阴离子的。
[1] Xiong X, Chen S, Shen J, et al. Cannabis suppresses antitumor immunity by inhibiting JAK/STAT signaling in T cells through CNR2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):99. Published 2022 Apr 6. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00918-y(IF:18.187)
[2] Zhang Z, Chen C, Yang F, et al. Itaconate is a lysosomal inducer that promotes antibacterial innate immunity [published online ahead of print, 2022 May 25]. Mol Cell. 2022;S1097-2765(22)00443-9. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.009(IF:17.970)
[3] Cai J, Peng J, Zang X, et al. Mammary Leukocyte-Assisted Nanoparticle Transport Enhances Targeted Milk Trace Mineral Delivery [published online ahead of print, 2022 Jun 30]. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;e2200841. doi:10.1002/advs.202200841(IF:17.521)
[4] Jin H, Liu K, Tang J, et al. Genetic fate-mapping reveals surface accumulation but not deep organ invasion of pleural and peritoneal cavity macrophages following injury. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2863. Published 2021 May 17. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23197-7(IF:14.919)
[5] Sheng D, Ma W, Zhang R, et al. Ccl3 enhances docetaxel chemosensitivity in breast cancer by triggering proinflammatory macrophage polarization [published correction appears in J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jun;10(6):]. J Immunother Cancer. 2022;10(5):e003793. doi:10.1136/jitc-2021-003793(IF:13.751)
[6] Zhao L, Zhang H, Liu X, et al. TGR5 deficiency activates antitumor immunity in non-small cell lung cancer via restraining M2 macrophage polarization. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(2):787-800. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.011(IF:11.614)
[7] Xia L, Zhang C, Lv N, et al. AdMSC-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury via transferring mitochondrial component to improve homeostasis of alveolar macrophages. Theranostics. 2022;12(6):2928-2947. Published 2022 Mar 21. doi:10.7150/thno.69533(IF:11.556)
[8] Zhang X, Hou L, Li F, et al. Piezo1-mediated mechanosensation in bone marrow macrophages promotes vascular niche regeneration after irradiation injury. Theranostics. 2022;12(4):1621-1638. Published 2022 Jan 16. doi:10.7150/thno.64963(IF:11.556)
[9] Wang H, Li L, Li Y, et al. Intravital imaging of interactions between iNKT and kupffer cells to clear free lipids during steatohepatitis. Theranostics. 2021;11(5):2149-2169. Published 2021 Jan 1. doi:10.7150/thno.51369(IF:11.556)
[10] Xun J, Du L, Gao R, et al. Cancer-derived exosomal miR-138-5p modulates polarization of tumor-associated macrophages through inhibition of KDM6B. Theranostics. 2021;11(14):6847-6859. Published 2021 May 3. doi:10.7150/thno.51864(IF:11.556)
[11] Zuo L, Li J, Zhang X, et al. Aberrant mesenteric adipose extracellular matrix remodeling is involved in adipocyte dysfunction in Crohn's disease: The role of TLR-4-mediated macrophages [published online ahead of print, 2022 Jun 16]. J Crohns Colitis. 2022;jjac087. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac087(IF:9.071)
[12] Huang C, Wang J, Liu H, et al. Ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate ameliorates colitis by promoting M2 macrophage polarization through the STAT6-dependent signaling pathway. BMC Med. 2022;20(1):148. Published 2022 Apr 15. doi:10.1186/s12916-022-02352-x(IF:8.775)
[13] Jiang P, Gao W, Ma T, et al. CD137 promotes bone metastasis of breast cancer by enhancing the migration and osteoclast differentiation of monocytes/macrophages. Theranostics. 2019;9(10):2950-2966. Published 2019 May 9. doi:10.7150/thno.29617(IF:8.063)
[14] Yang XL, Wang G, Xie JY, et al. The Intestinal Microbiome Primes Host Innate Immunity against Enteric Virus Systemic Infection through Type I Interferon. mBio. 2021;12(3):e00366-21. Published 2021 May 11. doi:10.1128/mBio.00366-21(IF:7.867)
[15] Sun Z, Huang W, Zheng Y, et al. Fpr2/CXCL1/2 Controls Rapid Neutrophil Infiltration to Inhibit Streptococcus agalactiae Infection. Front Immunol. 2021;12:786602. Published 2021 Nov 24. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.786602(IF:7.561)
[16] Cai J, Cui X, Wang X, You L, Ji C, Cao Y. A Novel Anti-Infective Peptide BCCY-1 With Immunomodulatory Activities. Front Immunol. 2021;12:713960. Published 2021 Jul 22. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.713960(IF:7.561)
[17] Li C, Song J, Guo Z, et al. EZH2 Inhibitors Suppress Colorectal Cancer by Regulating Macrophage Polarization in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2022;13:857808. Published 2022 Apr 1. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.857808(IF:7.561)
[18] Tian L, Li W, Yang L, et al. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Participates in Liver Inflammation by Promoting M1 Macrophage Polarization via RhoA/NF-κB p65 and ERK1/2 Pathways, Respectively, in Mouse Liver Fibrogenesis. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1214. Published 2017 Sep 28. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01214(IF:6.429)
[19] Wang X, Li W, Jiang H, et al. Zebrafish Xenograft Model for Studying Pancreatic Cancer-Instructed Innate Immune Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(12):6442. Published 2022 Jun 9. doi:10.3390/ijms23126442(IF:5.924)
[20] Xiong C, Zhu Y, Xue M, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(3):3386-3404. doi:10.18632/aging.202264(IF:5.682)
[21] Wang J, Li X, Wang Y, Li Y, Shi F, Diao H. Osteopontin aggravates acute lung injury in influenza virus infection by promoting macrophages necroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):97. Published 2022 Mar 4. doi:10.1038/s41420-022-00904-x(IF:5.241)
[22] Ma Y, Liang Y, Wang N, et al. Avian Flavivirus Infection of Monocytes/Macrophages by Extensive Subversion of Host Antiviral Innate Immune Responses. J Virol. 2019;93(22):e00978-19. Published 2019 Oct 29. doi:10.1128/JVI.00978-19(IF:5.103)
[23] Jiang Q, Li W, Zhu X, et al. Estrogen receptor β alleviates inflammatory lesions in a rat model of inflammatory bowel disease via down-regulating P2X7R expression in macrophages. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021;139:106068. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2021.106068(IF:5.085)
[24] Lu Y, Lu G, Gao L, et al. The Proresolving Lipid Mediator Maresin1 Alleviates Experimental Pancreatitis via Switching Macrophage Polarization. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:6680456. Published 2021 Mar 9. doi:10.1155/2021/6680456(IF:4.711)
[25] Li W, Chang N, Tian L, et al. miR-27b-3p, miR-181a-1-3p, and miR-326-5p are involved in the inhibition of macrophage activation in chronic liver injury. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017;95(10):1091-1105. doi:10.1007/s00109-017-1570-0(IF:4.686)
[26] Ji L, Chen Y, Xie L, Liu Z. The role of Dock2 on macrophage migration and functions during Citrobacter rodentium infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021;204(3):361-372. doi:10.1111/cei.13590(IF:4.330)
[27] Yang L, Dong C, Tian L, Ji X, Yang L, Li L. Gadolinium Chloride Restores the Function of the Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication between Hepatocytes in a Liver Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3748. Published 2019 Jul 31. doi:10.3390/ijms20153748(IF:4.183)
[28] Wu H, Xu X, Li J, Gong J, Li M. TIM‑4 blockade of KCs combined with exogenous TGF‑β injection helps to reverse acute rejection and prolong the survival rate of mice receiving liver allografts. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(1):346-358. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2018.3606(IF:4.101)
[29] Zhao J, Chen XD, Yan ZZ, Huang WF, Liu KX, Li C. Gut-Derived Exosomes Induce Liver Injury After Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion by Promoting Hepatic Macrophage Polarization [published online ahead of print, 2022 Jun 14]. Inflammation. 2022;10.1007/s10753-022-01695-0. doi:10.1007/s10753-022-01695-0(IF:4.092)
[30] Guan Z, Ding Y, Liu Y, et al. Extracellular gp96 is a crucial mediator for driving immune hyperactivation and liver damage. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12596. Published 2020 Jul 28. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69517-7(IF:3.998)
[31] Song C, Li H, Li Y, et al. NETs promote ALI/ARDS inflammation by regulating alveolar macrophage polarization. Exp Cell Res. 2019;382(2):111486. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.06.031(IF:3.329)
[32] Li R, Yang L, Jiang N, et al. Activated macrophages are crucial during acute PM2.5 exposure-induced angiogenesis in lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2020;19(1):725-734. doi:10.3892/ol.2019.11133(IF:1.871)